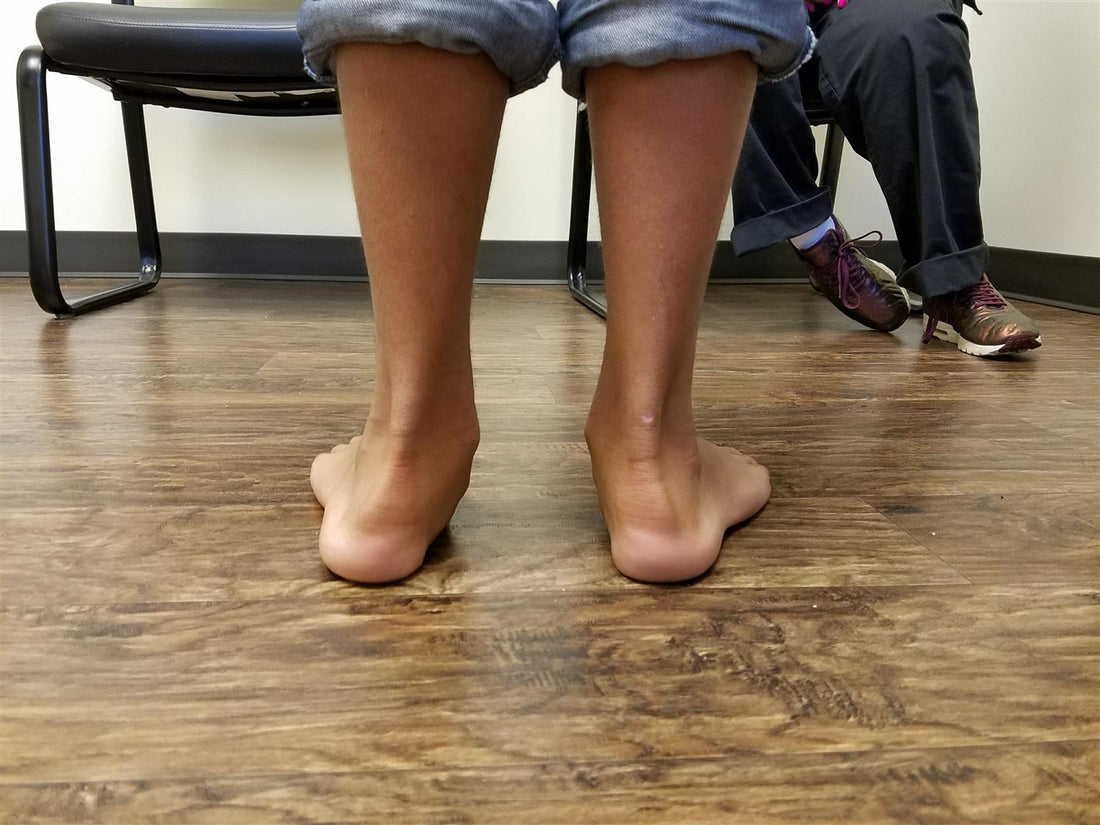
Managing Flexible Flatfoot: Considerations and Strategies
Due to the lack of agreement on the best management practices, flat foot, especially asymptomatic flexible flat foot, can be difficult for clinicians to treat. The management of both symptomatic and asymptomatic flexible flatfoot is examined in this article, along with the related issues and debates. It looks at the differences between observation and intervention, the function of orthotics and auxiliary shoe supports, and management techniques for symptomatic flexible flatfoot.

Considerations and Debates Regarding the Management of Asymptomatic Flexible Flatfoot
Intervention vs. Observational Approach
When there is no discomfort, neither nonoperative nor operative management is better than observation on its own.
The function of orthotics and supplemental shoe supports
For the treatment of asymptomatic flexible flatfoot, a variety of supportive devices have been investigated, including heel cups, wedges, silicone inserts, and bespoke orthotics.
There have been no discernible changes in reported outcomes or observed variations in foot development in studies assessing the effectiveness of orthotic use and shoe alterations.
Overall, because there is no data to definitively support therapies and because there may be dangers involved in administering unnecessary treatment, managing asymptomatic flexible flatfoot remains difficult.
Strategies and Considerations for the Management of Symptomatic Flexible Flatfoot
Symptoms of symptomatic flatfoot include calluses, lower leg pain, foot muscular fatigue, and fast shoe degeneration.
Additionally, patients may recur in their ankle sprains, especially while wearing supportive footwear, which calls for an orthopaedic surgeon's recommendation.
Nonoperative Management
Nonoperative methods, including rest, modifying activities, ice, massage, and anti-inflammatory drugs, are part of the first treatment.
Because orthotics press against the talar head, individuals with a tight Achilles tendon may find it difficult to tolerate them. In these cases, a home physical therapy programme that emphasizes calf muscle strengthening and Achilles tendon flexibility is necessary.
Role of Orthotics

When treating symptomatic flatfoot without a tight heel cord, orthotics may be the first line of treatment and may help some people feel less pain.
As they haven't proven to be any better than over-the-counter alternatives, custom orthotics are a sensible starting point for management.
Whether a patient has symptomatic or asymptomatic flatfoot, managing their condition necessitates carefully taking into account their unique preferences and medical history. For asymptomatic flexible flatfoot, the evidence for therapies is still ambiguous, but symptomatic instances require a customized strategy that includes nonoperative measures and, when needed, orthotics. Prioritizing patient comfort and functional outcomes, clinicians must negotiate the challenges associated with flatfoot care.
Weak muscles and inappropriate footwear choices frequently lead to pronation issues. Not sure which shoes to opt for? Check out our collection for tailored choices at DiabeticShoe.in