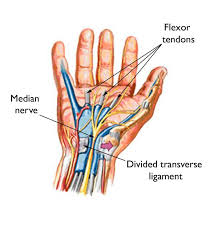
The human hand is a complex structure, intricately designed to perform a multitude of tasks. At the heart of its functionality lies a network of nerves that not only enable movement but also provide sensory feedback. Understanding the anatomy and function of the palm nerves is essential, particularly for those experiencing conditions like neuropathy or median nerve compression.
The palm is innervated by several major nerves: the median nerve, the ulnar nerve, and the radial nerve. Each of these nerves plays a unique role in the hand's functionality.
Median Nerve
The median nerve is often referred to as the "eye of the hand." It travels down the arm and into the hand, passing through the carpal tunnel at the wrist, a narrow passageway that can sometimes become a site of compression. This nerve is responsible for the sensation in the thumb, index finger, middle finger, and part of the ring finger. It also controls some of the muscles at the base of the thumb.
Ulnar Nerve
The ulnar nerve innervates the small muscles of the hand, providing sensation to the little finger and the adjacent half of the ring finger. It plays a crucial role in the fine motor skills required for tasks like typing or playing musical instruments.
Radial Nerve
The radial nerve primarily serves the back of the hand, extending into the thumb, index finger, and middle finger. It facilitates wrist and finger extension, enabling movements such as opening the hand or spreading the fingers.
Functionality and Importance
The nerves in the hand and fingers are crucial for both motor and sensory functions. They allow for precise movements and provide sensory feedback, which is essential for tasks ranging from gripping objects to feeling textures.
Sensory Functions
The sensory functions of the hand nerves enable us to feel touch, temperature, and pain. This feedback is vital for protecting the hand from injury. For instance, if you touch something hot, the sensory nerves will trigger an immediate reaction to pull away, preventing burns.
Motor Functions
Motor functions facilitated by the palm nerves include the ability to grasp, pinch, and manipulate objects. These functions are particularly important in daily activities such as writing, eating, and dressing.
Common Nerve-Related Conditions
The nerves of the hand can be susceptible to various conditions, especially due to repetitive motions or injury. Understanding these conditions can help in their prevention and management.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve is compressed at the wrist, leading to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand. This condition is common among people who perform repetitive tasks, such as typing or assembly line work.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy refers to nerve damage that can result in numbness, tingling, and pain. Diabetic neuropathy is a common form of this condition, often affecting both the hands and feet. Proper footwear, such as diabetic shoes or neuropathy footwear, can alleviate symptoms by providing additional support and reducing pressure on the nerves.
Ulnar Nerve Compression
Ulnar nerve compression, often referred to as "cubital tunnel syndrome," occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed, usually at the elbow. This can lead to numbness and tingling in the little and ring fingers and can affect grip strength.
Preventive Measures and Treatment
Taking care of the hand nerves involves both preventive measures and appropriate treatment options, especially for those with pre-existing conditions like diabetes or repetitive strain injuries.
Supportive Footwear
For individuals with neuropathy, wearing supportive shoes is crucial. Diabetic footwear and neuropathy shoes are designed to reduce pressure on the feet, improve balance, and prevent injuries, which can indirectly benefit nerve health in the hands.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Making ergonomic adjustments in daily activities can help prevent nerve compression. For instance, using ergonomic keyboards and mice can reduce strain on the wrist, minimising the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome.
Hand Exercises
Regular hand exercises can strengthen the muscles and improve nerve function. Simple stretches and movements can enhance flexibility and reduce the risk of nerve compression.
Medical Intervention
In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary. Treatments can range from physical therapy to surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy and function of the palm nerves is key to maintaining hand health and functionality. By recognising the role these nerves play and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce the risk of nerve-related conditions and improve their overall quality of life. Whether it's through supportive footwear, ergonomic adjustments, or targeted exercises, taking proactive steps can make a significant difference.