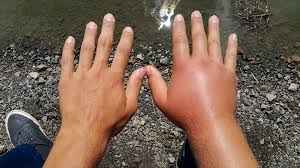
Hand swelling can be a frustrating and uncomfortable condition that affects your daily activities. Whether it's from overuse, injury, or an underlying health condition, understanding the causes and remedies for hand swelling is crucial. This article will guide you through the common causes, effective treatments, and preventive measures you can take to manage hand swelling and pain.
 Injury and Overuse
Injury and Overuse
One of the most common causes of hand swelling is injury or overuse. This can include sprains, fractures, or repetitive strain from activities like typing or playing an instrument. Such injuries often lead to inflammation, which causes swelling and pain in the affected area.
Arthritis
Arthritis is another prevalent cause of hand swelling. Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis lead to joint swelling and stiffness. These conditions occur when the cartilage in your joints wears down, causing bones to rub against each other, resulting in pain and swelling.
Infections
Infections in the hand, such as cellulitis or a cut that has become infected, can also cause swelling. These conditions require prompt medical attention to prevent the infection from spreading.
Fluid Retention
Fluid retention, often related to conditions like kidney disease or heart failure, can cause swelling in the hands. This is because excess fluid accumulates in the body tissues, leading to swelling.
Underlying Health Conditions
Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, can lead to hand swelling. Diabetic neuropathy, a complication of diabetes, can cause swelling and pain in the hands and feet.
Remedies for Hand Swelling
 Rest and Ice
Rest and Ice
For immediate relief from hand swelling due to injury or overuse, rest and ice are effective remedies. Rest the affected hand and apply ice wrapped in a cloth for 15-20 minutes every few hours. This helps reduce inflammation and swelling.
Elevation
Elevating your hand above the level of your heart can help reduce swelling by promoting blood flow and reducing fluid accumulation. Prop your hand on pillows or cushions when sitting or lying down.
Compression
Using a compression bandage can help manage swelling. Ensure the bandage is snug but not too tight to avoid cutting off circulation. Compression helps limit swelling by preventing fluid buildup in the tissues.
Medications
Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help reduce pain and swelling. For persistent or severe swelling, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or recommend specific hand pain relief medicines.
Hand Exercises and Physical Therapy
Gentle hand exercises can help improve mobility and reduce swelling. A physical therapist can guide you through exercises tailored to your condition, helping you strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
Proper Footwear
For those with diabetes or arthritis, wearing the right footwear is essential. Diabetic shoes and arthritis footwear provide the necessary support and cushioning to reduce stress on the joints and prevent swelling.
Preventive Measures
Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet, can help prevent conditions that lead to hand swelling. Exercise improves circulation, while a diet rich in vitamins and minerals supports overall joint health.
Manage Underlying Health Conditions
If you have a chronic condition like diabetes or arthritis, managing it effectively can prevent hand swelling. Follow your doctor's advice, take prescribed medications, and attend regular check-ups to keep your condition under control.
Protect Your Hands
If your job or hobbies involve repetitive hand movements, take regular breaks to rest your hands. Use ergonomic tools and equipment to reduce strain and prevent injuries that lead to swelling.
Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps prevent fluid retention, which can cause swelling. Staying hydrated ensures your body functions optimally and reduces the risk of swelling due to fluid buildup.
Avoid Excessive Salt Intake
High salt intake can lead to fluid retention and swelling. Limit your consumption of salty foods and choose low-sodium options to keep your blood pressure and fluid levels in check.
When to See a Doctor
While many cases of hand swelling can be managed with home remedies, it's important to seek medical attention if:
-
The swelling persists or worsens despite treatment
-
You experience severe pain or loss of function in the hand
-
There are signs of infection, such as redness, warmth, or pus
-
Swelling is accompanied by other symptoms like fever or difficulty breathing
Conclusion
Understanding the causes and remedies for hand swelling empowers you to take control of your health. By implementing effective treatments and preventive measures, you can reduce hand swelling and improve your quality of life. Remember, if you experience persistent or severe symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is crucial to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment. With the right approach, you can manage hand swelling effectively and maintain healthy, pain-free hands.