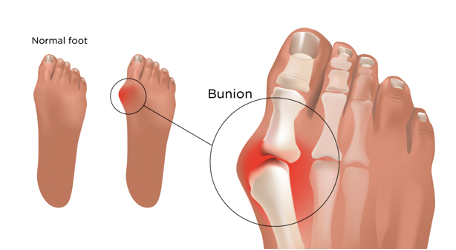
Battling Bunions: Understanding, Treating, and Preventing Foot Bunions for Happy, Healthy Feet
Bunions, those bony bumps that develop at the base of the big toe, can be more than a cosmetic concern—they can lead to discomfort, pain, and difficulty with shoe wear. Whether you've just noticed a small bump or have been dealing with bunions for a while, understanding their causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for maintaining foot health. In this comprehensive guide, we'll take a step-by-step approach to demystifying bunions.

What Causes Bunions?
- Genetics: A significant factor in bunion development is often hereditary, with a family history of bunions increasing the risk.
- Foot Structure: Abnormal foot structure or mechanics, such as flat feet or low arches, can contribute to bunion formation.
- Footwear: Wearing tight, narrow shoes, especially those with pointed toes, can exacerbate bunion progression.
- Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as arthritis, can contribute to the development of bunions.
Signs and Symptoms
- Bony Bump: The most noticeable sign is a bony bump at the base of the big toe.
- Pain and Swelling: Bunions can cause pain, inflammation, and redness around the joint.
- Change in Toe Alignment: The big toe may angle toward the second toe, causing misalignment.
Treatment Options
- Footwear Modification: Choose shoes with a wide toe box and low heels to reduce pressure on the bunion.
- Orthotic Inserts: Custom or over-the-counter orthotic inserts can help support the foot and correct imbalances.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers and ice packs can alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve foot strength and flexibility can be beneficial.
Prevention Tips
- Proper Footwear: Wear shoes with ample space for toes and avoid high heels.
- Foot Exercises: Perform regular exercises to strengthen and stretch the muscles in your feet.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight can contribute to bunion development, so maintaining a healthy weight is crucial.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If bunions cause persistent pain, or difficulty walking, or if conservative measures don't provide relief, consult with a healthcare professional or a podiatrist. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be considered.